Classification of Types of Graphene
| Type | Layers | Properties | Applications |
| Epitaxial CVD | 1-2 | Conductive/ Almost Transparent/ Optical Absorption | High end electronics/ Transparent electrodes(ITO) |
| FLG | 3-10 | Conductive/ Flexible/ Very High Surface Area | Sensors/Supercapacitors/ |
| GNPs | 11-100 | Refractories/ Lightweight, Wide aspect ratio, Attain Improved Barrier Characteristics and Enhanced Mechanical Properties | Composites/ Inks and Coating/ Lubricants/ Printing/ Thermoplastics/ Thermoset/ Rubber |
| GO | Various | Insulator/ Hydrophilic dispersion defect and void/Amorphous | Semiconductor/ Concrete/ |
| Graphite used in GNP production | 100+ | Absorption/ Insoluble in water/ Soft & Slippery | Engineering materials/ Lubricants |
Functionalization of Graphene
Graphene’s diverse properties do not perform at its best when combining with other materials until it has been functionalized to specific application or product. The process involves reducing the cohesiveness between graphene sheets and manipulating physical and chemical properties at the surface level.
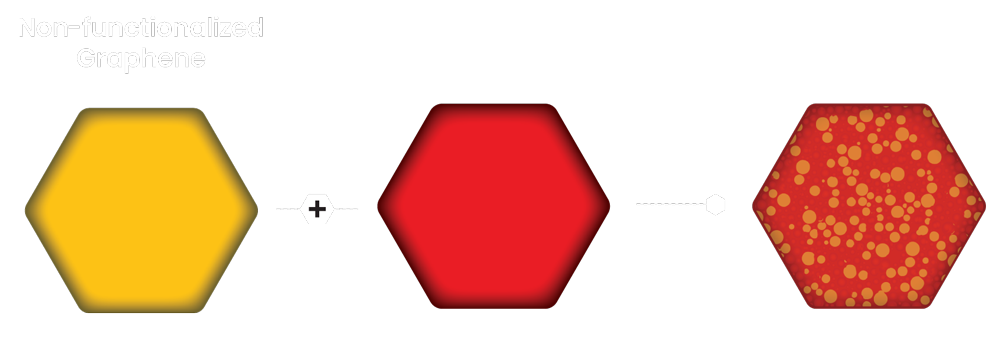
Inhomogeneous Mix
Incapable of utilizing
graphene properties

Homogeneous Mix
Allowing graphene
properties to enhance the
product/application
